Do You Know How to Use Fiber Optic Patch Cables? Unveiling the Various Types of Fiber Optic Patch Cables?

Fiber optic patch cords are used to make patch cords from equipment to fiber optic cabling links. There is a thicker protective layer, generally used in the connection between the optical terminal and the terminal box, used in fiber optic communication systems, fiber optic access networks, fiber optic data transmission, and local area networks and some other areas.

Fiber optic patch cords (also known as fiber optic connectors) refer to fiber optic cables that are fitted with connectors at both ends of the plug, used to achieve the optical path of the active connection; one end is fitted with a plug known as a pigtail. Fiber optic patch cable (Optical Fiber Patch Cord/Cable) and coaxial cable are similar, except that there is no mesh shield. The center is a glass core for light propagation. In multi-mode fiber, the core diameter is 50μm ~ 65μm, roughly equivalent to the thickness of human hair. The diameter of the core of a single-mode fiber is 8 μm ~ 10 μm. outside the core is surrounded by a layer of refractive index lower than the core of the glass envelope to keep the optical fiber inside the core. Then outside is a thin plastic jacket to protect the jacket.

The classification and overview of fiber optic patch cords are as follows
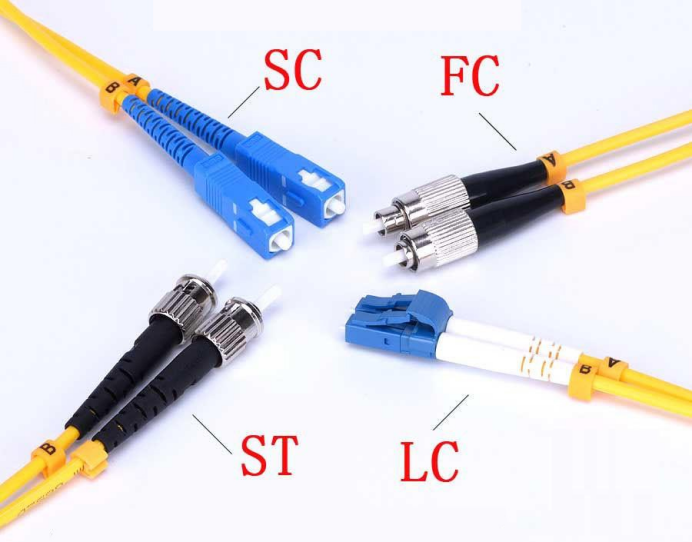
Fiber optic patch cords (also known as fiber optic connectors), that is, fiber optic connectors to access the optical module, there are also several kinds, and they are not interoperable with each other. the SFP module is connected to LC fiber optic connectors, while the GBIC is connected to SC fiber optic connectors. The following is a detailed description of several commonly used fiber optic connectors in network engineering:
① FC-type fiber optic patch cord: the external reinforcement is the use of a metal sleeve, fastening method for the screw buckle. Generally used on the ODF side (the most used on the distribution frame)
② SC-type fiber optic patch cord: connect the GBIC optical module connector, which has a rectangular shell, the fastening method is the use of plug-and-plug pin-latch type, which does not need to rotate. (The most used in router switches)
(iii) ST-type fiber optic patch cord: commonly used in fiber optic distribution frames, the shell is round, the fastening method is a screw buckle. (For 10Base-F connection, the connector is usually ST type. Commonly used in fiber optic distribution frames)
④ LC type fiber optic patch cable: a connector for connecting the SFP module, it is made with a modular jack (RJ) latch mechanism which is easy to operate. (commonly used in routers)

1. According to the connection head can be divided into: FC, ST, SC, LC, MU, MPO, E2000, MTRJ, SMA, etc., the end face contact mode PC, UPC, APC.
2.Fiber outer diameter Ф0.9mm, Ф2mm, Ф3mm, fiber core: single-core, double-core, 4-core, 6-core, 8-core, 12-core or customer-specific.
3. Fiber types can be divided into: G652B, G652D, G655, G657A1, G657A2, 50/125, 62.5/125, OM3 (50/125-150), OM4 ( 50/125-300), and so on.
4. Connector color can be divided into the blue (commonly used in single-mode PC, UPC connector), beige, gray (commonly used in multi-mode connector), green (APC connector), aqua blue (OM3), the color of the tail sleeve can be divided into gray, blue, green, white, red, black, lime green.
5. Connection line length: customized.

Single-mode fiber optic patch cable
Single Mode Fiber (SingleModeFiber): the center glass core is very thin (core diameter is generally 9 or 10μm), and can only transmit a mode of fiber. Therefore, its intermodal dispersion is very small, suitable for long-distance communication, but there are also material dispersion and waveguide dispersion, so that the single-mode fiber on the spectral width of the light source and the stability of the higher requirements, that is, the spectral width should be narrow, the stability should be good. Later it was found that at 1.31 μm wavelength, the material dispersion and waveguide dispersion of the single-mode fiber is positive and negative, and the size is exactly equal. In this way, the 1.31 μm wavelength region has become an ideal working window for optical fiber communications, but also the main working band of the current practical fiber optic communication system 1.31 μm conventional single-mode optical fiber is the main parameter is determined by the International Telecommunication Union ITU-T in the G652 recommendations, so this fiber is also known as the G652 fiber.
Single-mode fibers can support longer transmission distances than multimode fibers and can support transmission distances of more than 5000m in 100Mbps Ethernet to 1Gigabit networks.
From a cost perspective, single-mode fiber is more expensive than multimode fiber optic cables, as fiber optic terminators are very expensive.
The refractive index distribution is similar to that of mutant fiber, the core diameter is only 8~10 μm, and the light propagates in a straight line along the central axis of the core. Because this kind of fiber can only transmit one mode (two polarization states are simply merged), so it is called single-mode fiber, and its signal distortion is very small.
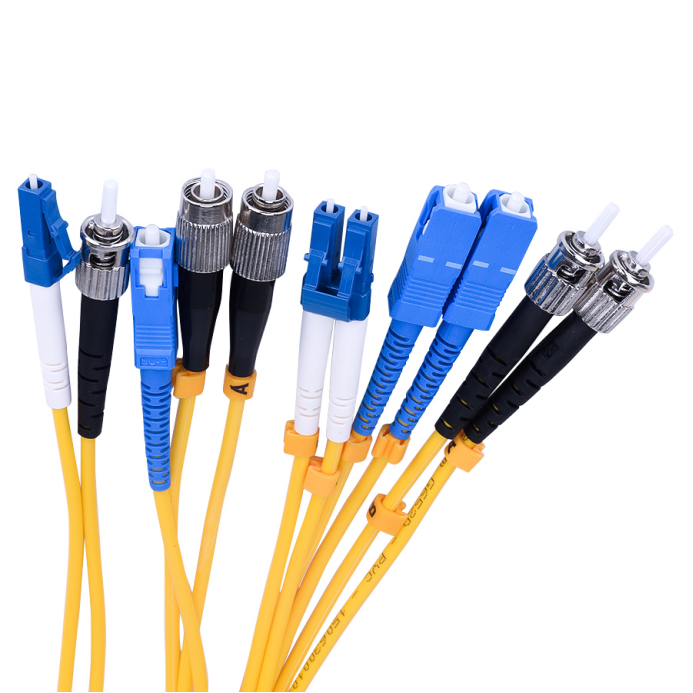

Multimode Fiber Patch Cord
The nominal diameter specification of the core of the multimode fiber is 62.5μm/125μm. or 50μm/125μm. The specifications (number of cores) are 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72, 84, 96 cores and so on. Cable outer sheath materials are ordinary type; ordinary flame retardant; low smoke halogen free type; and low smoke halogen free flame retardant type.
There are two kinds of multimode fiber, one gradient type (graded) and the other step type (stepped), for gradient type (graded) fiber, the core of the refractive index (refraction index) in the core of the periphery of the smallest and gradually to the center of the point is increasing, to reduce the signal mode dispersion, and for the stepped type (Stepped) Index) fiber optic cable, the refractive index is an average of the same, and only in the cladding (cladding) surface will be suddenly reduced. Stepped fiber generally has a lower bandwidth than graded fiber. In network applications, the most popular multimode fiber is 62.5/125, 62.5/125 means that the core diameter of the fiber is 62.5 μm and the cladding (cladding) diameter of 125 μm, the other more common 50/125 and 100/140.
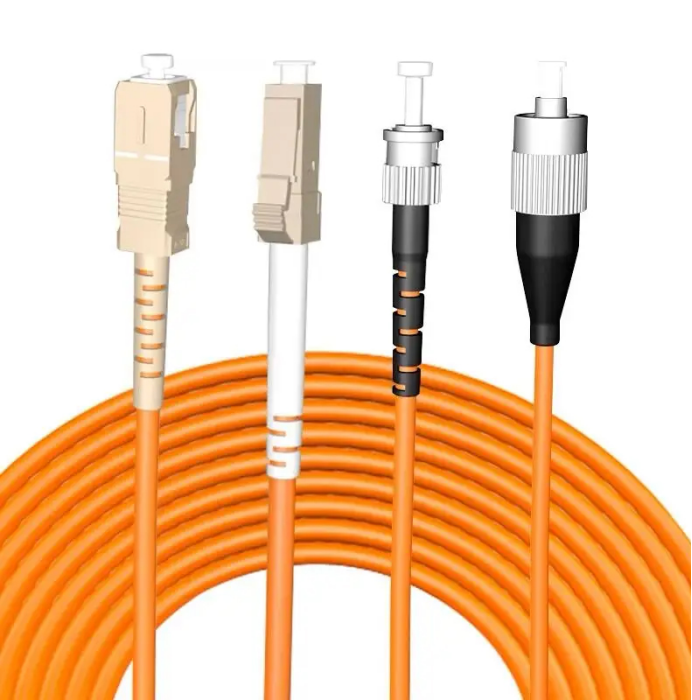

APC Single-mode fiber optic patch cords
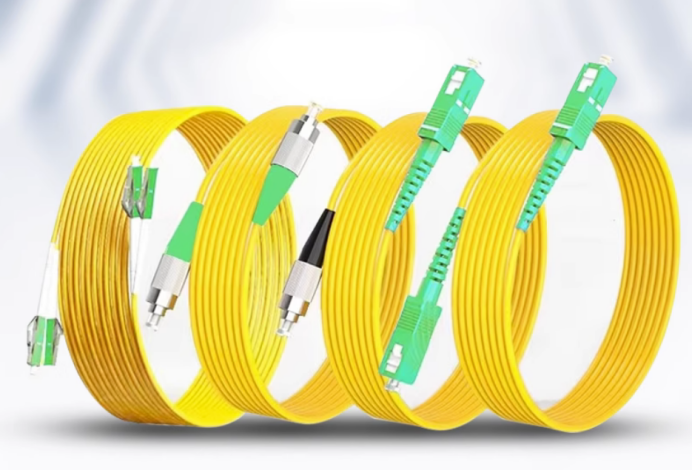

OM3 Multimode Fiber Optic Patch Cords
OM3 multimode fiber optic cable is made of OM3 multimode fiber with indoor or outdoor sheath, commonly used in building construction backbone laying and close to the backbone connection between two buildings.
OM stands for Multi-mode fiber (Multi-mode fiber, also known as MMF), usually, there are four grades of OM1/OM2/OM3/OM4, the main difference lies in the mode bandwidth of the 850nm transmission window.
OM2, OM3, and OM4 fibers belong to the same IEC 60793-20 specified A1a type of fiber, A1a type of fiber using a 50/125 structure, 50 μm core and 125 μm cladding, OM2 for the A1a.1, OM3 for the A1a.2, OM4 for the A1a.3, OM3 and OM4 for the laser-optimized fiber type can be in the 850 nm transmission window to provide higher transmission bandwidth.
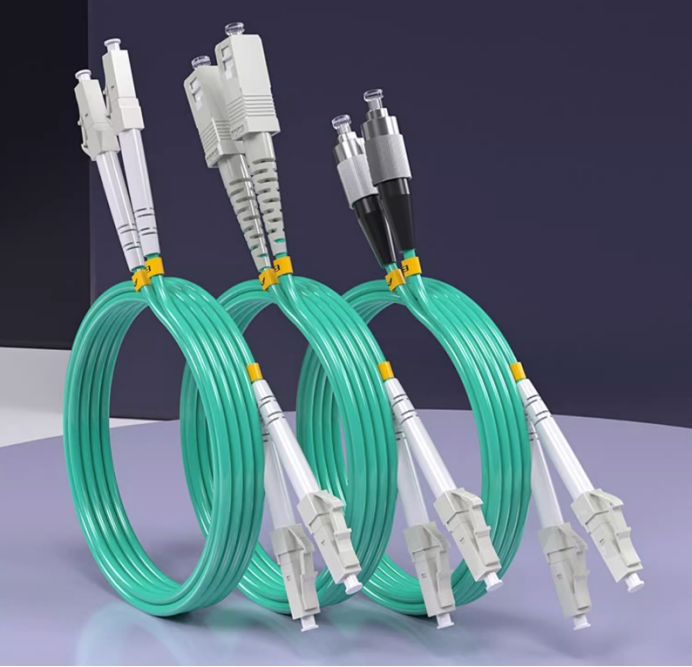
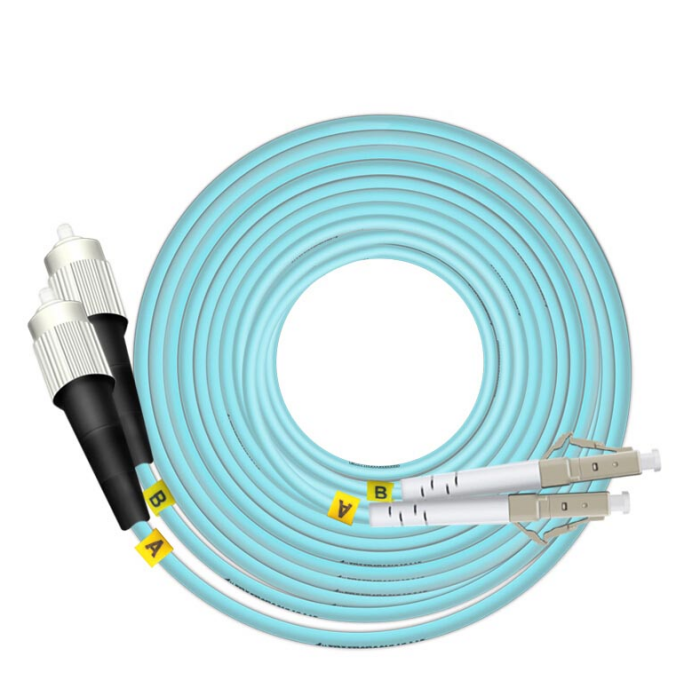


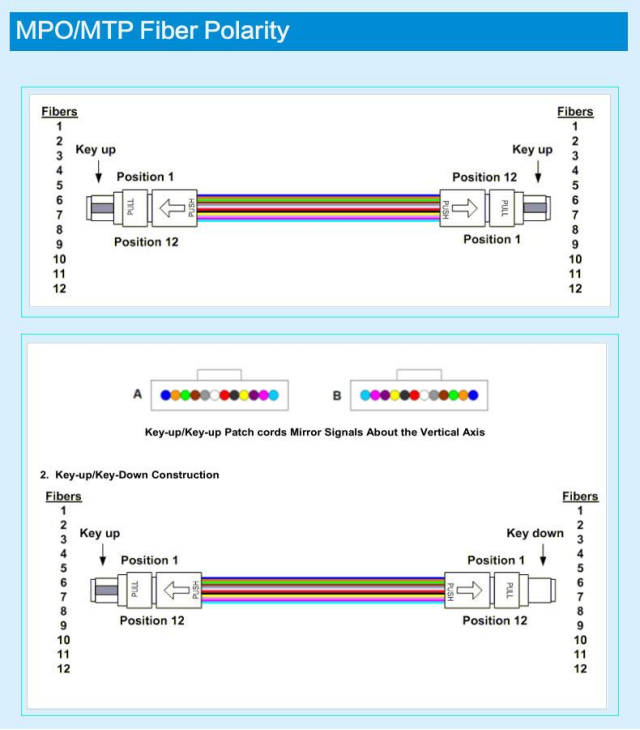
MPO Fiber Optic Patch Cords
MPO (Multi-fiberPushOn) connector is one of the MT series connectors, MT series of inserts are used on the insert end face of the left and right two guide holes with a diameter of 0.7mm and guide pin (also known as the PIN pin) for precise connection. MPO connectors and fiber optic cable processing can produce various forms of MPO patch cords. MPO patch cords can have a 2~12 core design, up to 24 cores, and currently can be used in a variety of applications, such as fiber optic cables. MPO patch cords can have 2~12 cores design, and up to 24 cores, currently the most used MPO connector is 12 cores.MPO connector’s compact design, so that the MPO jumper cores, are small in size.MPO jumper cords are widely used in the cabling process in the need for high-density integration of fiber optic lines in the environment, the FTTX and 40/100GSFP, SFP +, and other transceiver modules or equipment inside and outside of the connection applications.
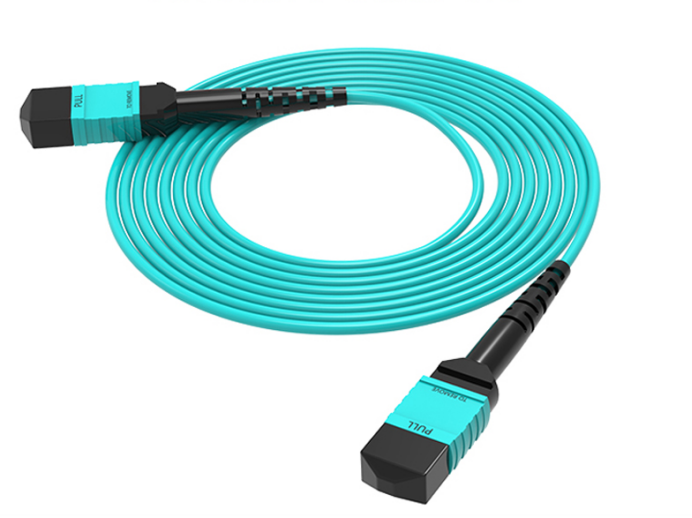

MPO Fiber Optic Patch Cords

MPO (Multi-fiberPushOn) connector for one of the MT series connectors, MT series of inserts are used on the insert end face of the left and right of the two 0.7mm diameter guide holes and guide pins (also known as PIN pins) for accurate connection.MPO connectors and fiber optic cable processing can produce a variety of forms of MPO patch cords.MPO patch cords can have a 2 ~ 12-core design, and up to 24-core, and currently, the MPO patch cord can be used in a variety of applications, such as FTTX and 40/100GSFP SFP+ transceiver modules or equipment internal and external connection applications. MPO patch cords can have 2~12 cores design, up to 24 cores, currently, the most used is 12 cores MPO connector.MPO connector’s compact design, so that the MPO jumper cores, are small in size.MPO jumper cords are widely used in the cabling process and require high-density integration of fiber optic lines in the environment, the FTTX and 40/100GSFP, SFP + transceiver modules, or equipment inside and outside of the connection application.

MPO (Multi-fiber Push On) collectively referred to as the MT series connectors MT series of inserts are used on the insert end of the surface of the left and right two guide holes with a diameter of 0.7mm and guide pins (also known as PIN pins) for the exact connection MPO can be 2 ~ 12-core design, but it can also be 24-core!
Currently, the more commonly used connector is the 12-pole connector
MPO’s compact design, so that the number of cores, and small size is widely used in the wiring process requires high-density integration of fiber optic lines in the environment of FTTX and 40/100GSFP, SFP + transceiver equipment, such as the internal connection applications of the company can provide a variety of adapter and non-adapter MPO patch cords, adapter MPO a wide range of types of ribbons, bundles, through the branching (round or square) can be adapted to the 2~24 cores of 0.9 or 2.0 fiber optic cable branches, the type of connector can be specified by the customer, the length and other requirements can be selected by the customer products are by Telcordia-GR-326, IEC standards, and Rohs requirements.

Ribbon Fiber Patch Cords
Ribbon fiber optic patch cords, that is, the ready-made ribbons on both ends of a good fiber optic connector, there can be FC, SC, and other interfaces, the current market is mostly SC-SC interfaces, the other FC-SC, and FC-FC are also produced. Skinned fiber optic patch cords are also known as skinned patch cords, skinned patch cords, FTTH butterfly pigtails, SC-type dual-ended prefabricated into the end of the skinned fiber optic patch cords, FTTH prefabricated skinned fiber optic patch cords, and so on.
Customized specifications of the skin cable: 3m, 5m, 10m, 20m, 30m, 40m, 50m, 60m, 80m, 100m, 150m, 200m, 300m, 500m, 800m allow can be customized.
Usage:
◆ Telecommunication network, data transmission, test equipment, local area network (LAN), broadcasting television network (CATV)
Features:
◆ Connector connector type has FC.SC.ST.LC etc. End face contact types are PC.UPC.APC type. High-quality zirconium dioxide ceramic core, low insertion loss, good interchangeability.
◆ Leather jumper cables (pigtail) can be spliced with a fiber optic activity connector or through fusion splicing to achieve fiber optic quick connection function, compared with fiber optic quick connector, the reliability of the connection, stability, service life, installation success rate, technical indicators, etc., have significantly improved; and the construction speed, the use of simple and convenient maintenance, lower costs

Armored Fiber Optic Cable
Since the introduction of optical fiber, due to the optical fiber itself, the material of the optical fiber used in a variety of environments, the optical fiber must be processed into a fiber optic cable with the corresponding mechanical properties to ensure that the optical fiber in the process of laying, installation, use, maintenance to ensure their safety, to ensure the smooth flow of the network. The fiber itself in the side pressure and impact resistance, is the very weak link. The existing large number of outdoor fiber optic cables, and indoor fiber optic cables, in complex environments do not give a fundamental guarantee of these properties.
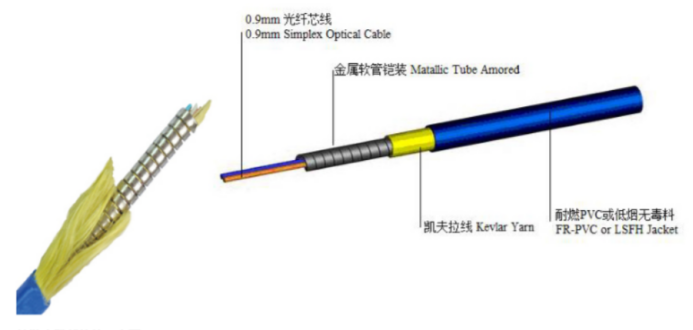
The introduction of the “flexible metal-clad fiber optic line” is the bare optical fiber, as well as a variety of specifications of the tight set of optical fiber through a special process, with a certain structural design, in the optical fiber around the cloak of a layer of flat profile of the spiral stainless steel material, in the optical fiber itself does not affect the superior optical properties of the fiber itself, and greatly improve the optical fiber line itself, the lateral compression resistance. fLine itself the ability to resist lateral pressure.
Tests have shown that the flexible metal-clad optical fiber’s resistance to lateral pressure, with the reduction of the outer diameter of the armored tube increases, the maximum value has reached the current conventional optical cable test equipment, the extreme value (8000N/10CM). The special fiber optic line processed into a variety of specifications of indoor and outdoor fiber optic cables can easily do small size, lightweight, superior environmental characteristics. It is the first choice of optical transmission products for building wiring, optical connection of key equipment room, field operation, sensor detection, fiber to the home, fiber to the desktop, and other complex environmental conditions.

FTTA Base Station Fiber Optic Patch Cords
Unlike ordinary indoor cabling fiber optic patch cords, first of all, due to the connection between RRU and BBU, most of the cables are in the outdoor environment for a long time, which requires fiber optic patch cords to be able to adapt to the performance of the regular outdoor environment, such as waterproof, sunscreen, aging resistance, strong tensile strength and so on. And fiber optic cable in the FTTA base station cabling environment, usually requires fiber optic cable to have good bending performance, to ensure the strength of the case, but also to ensure a certain degree of flexibility, easy to construct.
FTTA: Fiber to the antenna.
Fiber optic patch cord interface type PC, APC, UPC
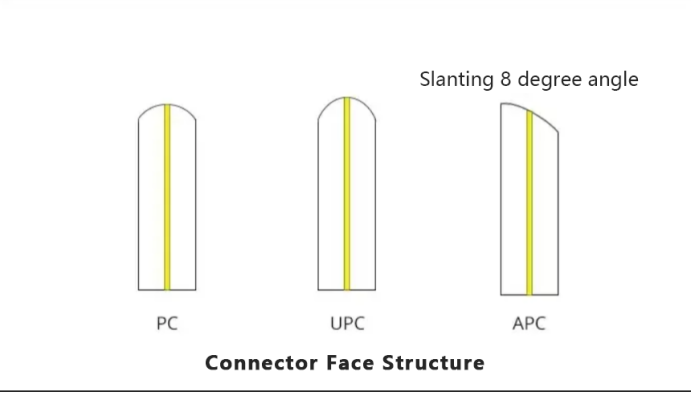
To make better contact between the end faces of two optical fibers, the core end face of fiber optic patch cords is usually ground into different structures. The common grinding methods are PC, APC, and UPC. PC/APC/UPC represents the front face structure of ceramic ferrule.
Different grinding angles of the end face
PC is Physical Contact, PC is micro-spherical grinding and polishing, the surface of the insert is ground into a slight sphere, and the fiber core is located a the highest point of the bend, which can effectively reduce the air gap between the fiber optic components, so that the two fiber optic end face to achieve physical contact.
UPC (Ultra Physical Contact), the UPC connector end face is not completely flat, there is a slight curvature to achieve a more accurate docking, UPC is based on the PC’s more optimized end face polishing and surface finish, and the end face looks more dome-shaped.
APC (Angled Physical Contact) is a term used to describe a beveled physical contact, where the fiber end face is typically ground to an 8° bevel. 8° angled bevels allow the fiber end face to be more tightly packed and reflect light through the angle of the bevel into the cladding instead of directly back to the light source, providing a better connection performance.